New Horizons spacecraft reaches farthest point ever visited
NASA’s New Horizons spacecraft flew past Ultima Thule in the early hours of New Year’s Day, ushering in the era of exploration from the enigmatic Kuiper Belt, a region of primordial objects that holds keys to understanding the origins of the solar system, the Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) announced January 1.
“Congratulations to NASA’s New Horizons team, Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory and the Southwest Research Institute for making history yet again. In addition to being the first to explore Pluto, today New Horizons flew by the most distant object ever visited by a spacecraft and became the first to directly explore an object that holds remnants from the birth of our solar system,” said NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine. “This is what leadership in space exploration is all about.”
Signals confirming the spacecraft is healthy and had filled its digital recorders with science data on Ultima Thule reached the mission operations center at APL at 10:29 a.m. EST on January 1, almost exactly 10 hours after New Horizons’ closest approach to the object.
“New Horizons performed as planned today, conducting the farthest exploration of any world in history — 4 billion miles from the Sun,” said Principal Investigator Alan Stern, of the Southwest Research Institute in Boulder, Colorado. “The data we have look fantastic and we’re already learning about Ultima from up close. From here out the data will just get better and better!”
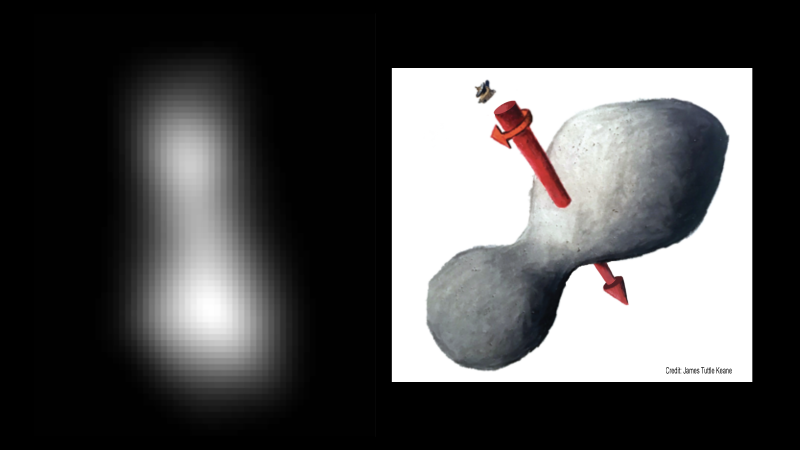
Images taken during the spacecraft’s approach — which brought New Horizons to within just 2,200 miles (3,500 kilometers) of Ultima at 12:33 a.m. EST — revealed that the Kuiper Belt object may have a shape similar to a bowling pin, spinning end over end, with dimensions of approximately 20 by 10 miles (32 by 16 kilometers). Another possibility is Ultima could be two objects orbiting each other. Flyby data have already solved one of Ultima’s mysteries, showing that the Kuiper Belt object is spinning like a propeller with the axis pointing approximately toward New Horizons. This explains why, in earlier images taken before Ultima was resolved, its brightness didn’t appear to vary as it rotated. The team has still not determined the rotation period.
As the science data began its initial return to Earth, mission team members and leadership reveled in the excitement of the first exploration of this distant region of space.
“New Horizons holds a dear place in our hearts as an intrepid and persistent little explorer, as well as a great photographer,” said Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory Director Ralph Semmel. “This flyby marks a first for all of us — APL, NASA, the nation and the world — and it is a great credit to the bold team of scientists and engineers who brought us to this point.”
“Reaching Ultima Thule from 4 billion miles away is an incredible achievement. This is exploration at its finest,” said Adam Hamilton, president and CEO of the Southwest Research Institute in San Antonio. “Kudos to the science team and mission partners for starting the textbooks on Pluto and the Kuiper Belt. We’re looking forward to seeing the next chapter.”
The New Horizons spacecraft will continue downloading images and other data in the days and months ahead, completing the return of all science data over the next 20 months. When New Horizons launched in January 2006, George W. Bush was in the White House, Twitter had just been launched and Time magazine’s Person of the Year was “you — all the worldwide web users.” Nine years into its journey, the spacecraft began its exploration of the Kuiper Belt with a flyby of Pluto and its moons. Almost 13 years after the launch, the spacecraft will continue its exploration of the Kuiper Belt until at least 2021. Team members plan to propose more Kuiper Belt exploration.
Source: APL







